Clearbit Webhooks
To integrate Clearbit webhooks with ngrok:
This guide covers how to use ngrok to integrate your localhost app with Clearbit by using Webhooks. Clearbit webhooks can be used to notify an external application whenever specific events occur in your Clearbit account.
By integrating ngrok with Clearbit, you can:
- Develop and test Clearbit webhooks locally, eliminating the time in deploying your development code to a public environment and setting it up in HTTPS.
- Inspect and troubleshoot requests from Clearbit in real-time via the inspection UI and API.
- Modify and Replay Clearbit Webhook requests with a single click and without spending time reproducing events manually in your Clearbit account.
- Secure your app with Clearbit validation provided by ngrok. Invalid requests are blocked by ngrok before reaching your app.
Step 1: Start your app
For this tutorial, we'll use the sample NodeJS app available on GitHub.
To install this sample, run the following commands in a terminal:
Loading…
This will get the project installed locally.
Now you can launch the app by running the following command:
Loading…
The app runs by default on port 3000.
You can validate that the app is up and running by visiting http://localhost:3000. The application logs request headers and body in the terminal and responds with a message in the browser.
Step 2: Launch ngrok
Once your app is running successfully on localhost, let's get it on the internet securely using ngrok!
-
If you're not an ngrok user yet, just sign up for ngrok for free.
-
Go to the ngrok dashboard and copy your Authtoken.
Tip: The ngrok agent uses the auth token to log into your account when you start a tunnel. -
Start ngrok by running the following command:
Loading…
-
ngrok will display a URL where your localhost application is exposed to the internet (copy this URL for use with Clearbit).
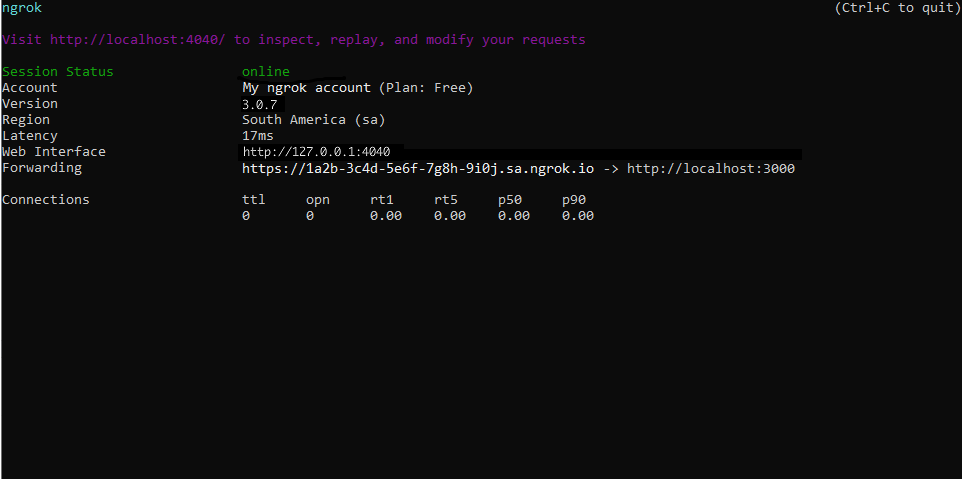
Step 3: Integrate Clearbit
To register a webhook on your Clearbit account follow the instructions below:
-
Access the Clearbit API Dashboard and sign in using your Clearbit account.
-
On the API Settings section, enter the URL provided by the ngrok agent to expose your application to the internet in the Webhook URL field (i.e.
https://1a2b-3c4d-5e6f-7g8h-9i0j.ngrok.app).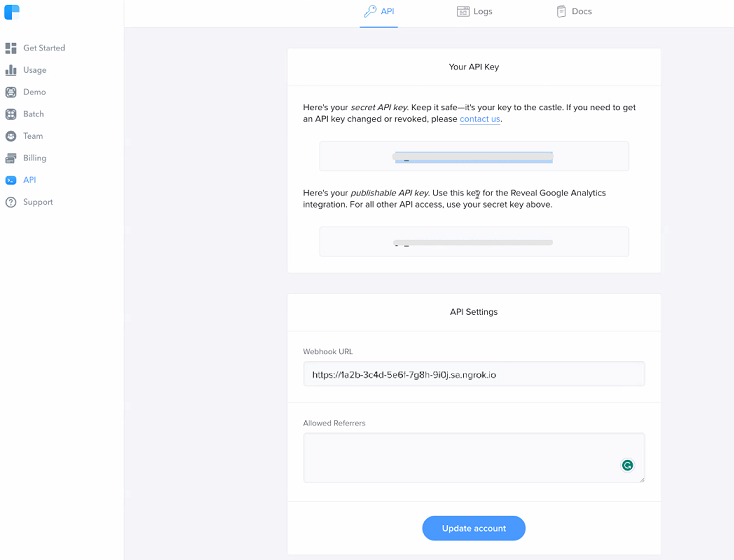
-
Click Update account.
-
Make note of the value of the Secret API Key that appears on the Clearbit API Dashboard page. Note: Usually the secret key value starts with
sk_.
Run Webhooks with Clearbit and ngrok
Clearbit sends different request body contents depending on the event that is being triggered. You can trigger new calls from Clearbit to your application by following the instructions below.
-
Open a terminal window and run the following command to gather information about your account:
Loading…
Note: Replace the following with values copied on previous steps:
- EMAIL_ADDRESS: An email address of a user in your Clearbit account organization.
- TOKEN: The Clearbit secret key you copied before.
Confirm your localhost app receives a notification and logs both headers and body in the terminal.
Inspecting requests
ngrok's Traffic Inspector captures all requests made through your ngrok endpoint to your localhost app. Click on any request to view detailed information about both the request and response.
By default, accounts only collect traffic metadata to avoid exposing secrets. You must enable full capture in the Observability section of your account settings to capture complete request and response data.
Use the traffic inspector to:
- Validate webhook payloads and response data
- Debug request headers, methods, and status codes
- Troubleshoot integration issues without adding logging to your app
Replaying requests
Test your webhook handling code without triggering new events from your service using the Traffic Inspector's replay feature:
-
Send a test webhook from your service to generate traffic in your Traffic Inspector.
-
Select the request you want to replay in the traffic inspector.
-
Choose your replay option:
- Click Replay to send the exact same request again
- Select Replay with modifications to edit the request before sending
-
Modify the request (optional): Edit any part of the original request, such as changing field values in the request body.
-
Send the request by clicking Replay.
Your local application will receive the replayed request and log the data to the terminal.
Secure webhook requests
The ngrok signature webhook verification feature allows ngrok to assert that requests from your Clearbit webhook are the only traffic allowed to make calls to your localhost app.
Note: This ngrok feature is limited to 500 validations per month on free ngrok accounts. For unlimited, upgrade to Pro or Enterprise.
This is a quick step to add extra protection to your application.
-
Access the Clearbit API Dashboard and sign in using your Clearbit account.
-
Copy the value of the Secret API Key field that appears on the screen. Note: Usually the secret key value starts with
sk_. -
Create a file named
clearbit_policy.yml, replacing{your api key}with the value you copied before:Loading…
-
Restart your ngrok agent by running the command:
Loading…
-
Repeat the command to gather information about your account.
Verify that your local application receives the request and logs the information to the terminal.